For every small business owner, risk management is a crucial consideration, and opting to buy small business insurance is one of the most straightforward and effective ways to achieve that. The proper insurance coverage not only assists in launching your business but also supports its growth into a thriving enterprise.
Selecting the right small business insurance is an essential component of any business strategy. However, the process can be daunting, especially for those who are new to purchasing insurance coverage.
Small business insurance plays a crucial role in safeguarding your business against various liabilities and risks. This coverage extends to claims stemming from:
- Bodily injuries
- Property damage
- Professional errors
- Natural disasters
In the absence of this insurance protection, you would be responsible for covering the costs of these claims with your personal assets. Unfortunately, in many instances, this financial burden forces small business owners to shut down their enterprises permanently. Therefore, if you’re inquiring about how to secure small business insurance, continue reading for guidance.
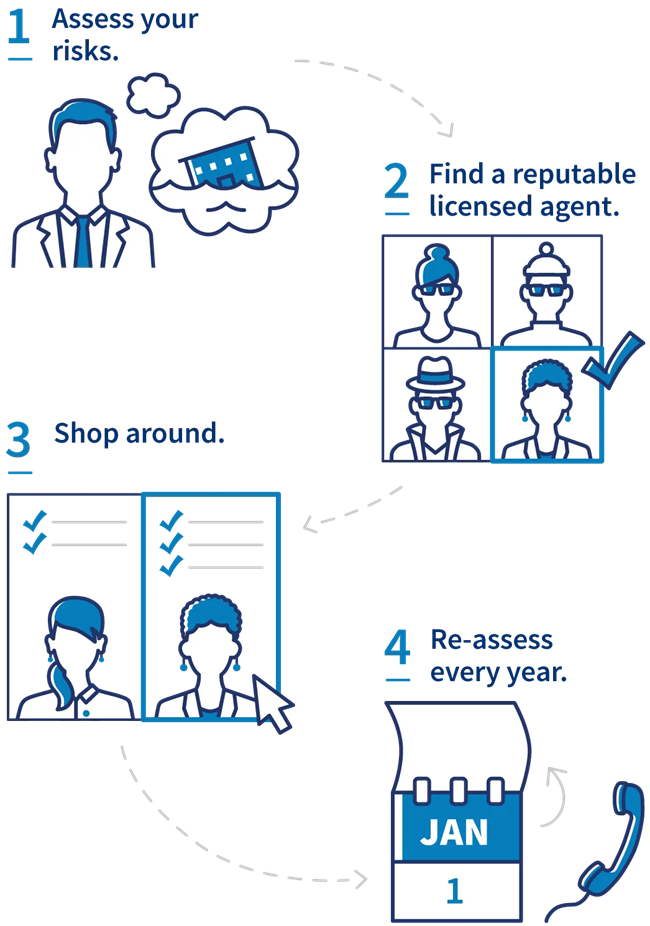
Four steps to buy small business insurance
Follow these steps to evaluate the most suitable types of insurance for your business and to obtain the necessary coverage to ensure comprehensive protection and risk mitigation. The information below is sourced from the U.S. Small Business Administration. For further insights into insurance matters, explore their website.
1. Assess your risks
Insurance companies engage in the process of underwriting to assess the level of risk they are willing to assume when issuing policies. During underwriting, your application is thoroughly reviewed to determine whether the insurance provider will offer full or partial coverage for the requested policies.
Each underwritten policy comes with both a premium and a deductible. The premium represents the cost of your insurance, and it can vary significantly among insurance companies. It depends on various risk factors, including your business location, building type, the availability of local fire protection services, and the amount of insurance you wish to purchase.
On the other hand, a deductible is the sum of money you agree to pay when filing a claim. Generally, the higher the deductible you are willing to bear, the lower your premium will be. However, opting for a high deductible means taking on some financial risk, so it’s crucial to evaluate your own risk tolerance before embarking on your insurance search.
2. Find a reputable licensed agent
Commercial insurance brokers play a valuable role in locating policies that align with your business requirements. These brokers earn commissions from insurance companies for policy sales, making it crucial to identify a reputable broker who prioritizes your needs alongside their own. Ensuring that your broker comprehends all the risks linked to your business is essential.
Securing an adept insurance agent holds the same weight as finding a skilled lawyer or accountant. It is imperative to seek an agent with a valid license, as state governments oversee and license insurance brokers. Many states offer directories of licensed agents for your reference.
3. Shop around
The National Federation of Independent Businesses offers valuable insights for insurance selection, aiding you in evaluating your business risks and ensuring comprehensive coverage. The scope and pricing of insurance can differ among insurance companies. Certain brokers specialize in providing insurance tailored to specific business types, while others can link you with policies that suit your specific business activities.
For instance, if you run a tow truck service, it’s advisable to seek an agent with expertise in securing policies designed for automotive service businesses. Specialized brokers often excel in obtaining optimal coverage and competitive rates for your needs.
4. Re-assess every year
Regularly reviewing your insurance coverage is a vital practice for your business’s financial security. As your business expands, your liabilities grow in tandem.
To avoid the risk of being underinsured in case of unforeseen disasters, it’s crucial to reach out to your insurance broker whenever you acquire new equipment, make replacements, or extend your operations. This allows you to keep your insurance coverage aligned with your evolving business needs.
Pro Tip
To determine the appropriate insurance coverage for your needs, seek advice from industry experts and consult with peers in your field.
Types of Small Business Insurance
Small businesses have various insurance options to choose from, tailored to their specific needs. Here’s a concise overview of the most common types of business insurance:
1. Business Income Insurance:
This type of insurance safeguards your business’s income in the event of a loss due to property damage, which leads to reduced productivity or service suspension. It doesn’t typically cover weather-related damage, as that’s usually handled by commercial property insurance.
2. Business Liability Insurance:
Ideal for small and midsize businesses, this insurance protects your personal assets if you’re sued. Even if your business is an LLC, it won’t provide this protection.
3. Business Owner’s Policy (BOP):
A BOP combines property and general liability insurance. It’s suitable for SMB owners who work in a space they own, such as their primary residence. If you regularly see clients at your home or work from a home office, a BOP may be appropriate.
4. Commercial Property Insurance:
Small and midsize businesses with substantial physical assets usually require commercial property insurance. The policy’s cost and structure depend on the specifics of your assets. The more property you cover, the higher the plan’s cost.
5. Contractors Professional Liability Insurance:
If your business relates to construction, building, or similar services, you’ll need professional liability insurance, particularly contractors professional liability insurance. It covers errors that may lead to legal action and liability claims for environmental impact.
6. Cyber Insurance:
This type of insurance is crucial if your company experiences a data breach. It covers the costs associated with liability in cases of stolen customer data, such as credit card information, Social Security numbers, or health records protected by HIPAA.
7. Employment Practices Liability Insurance:
SMB owners with employees can purchase this insurance, protecting them in cases of wrongful employment practices, such as discrimination, sexual harassment, and wrongful termination.
8. Errors and Omissions (E&O) Insurance:
Also known as professional liability insurance, E&O insurance is for businesses that provide professional services, protecting them from claims that their services caused financial harm to their clients. This is commonly sought after by consultants and financial services professionals.
9. General Liability Insurance:
It safeguards your company if you face claims related to property damage, personal injuries, or advertising injuries. It doesn’t typically cover the liabilities handled by cyber insurance.
10. Workers’ Compensation Insurance:
This insurance helps cover employees’ medical expenses and lost wages due to on-the-job injuries or illnesses. Unlike other insurance types, workers’ comp is mandatory in every state except Texas.
Conclusion
While most of your business endeavors yield positive results, occasional mishaps can occur. In rare instances, these mishaps can escalate into significant issues, potentially leaving you with substantial financial liabilities. Business insurance serves as a valuable tool to mitigate or even eliminate these financial burdens during challenging circumstances.

